Bispecific antibodies are an exciting new class of therapeutics permitting simultaneous engagement of two distinct targets with the same antibody. A wide array of protein engineering options exist to create bispecific (or higher order multispecific) antibody constructs, some of which are shown here.
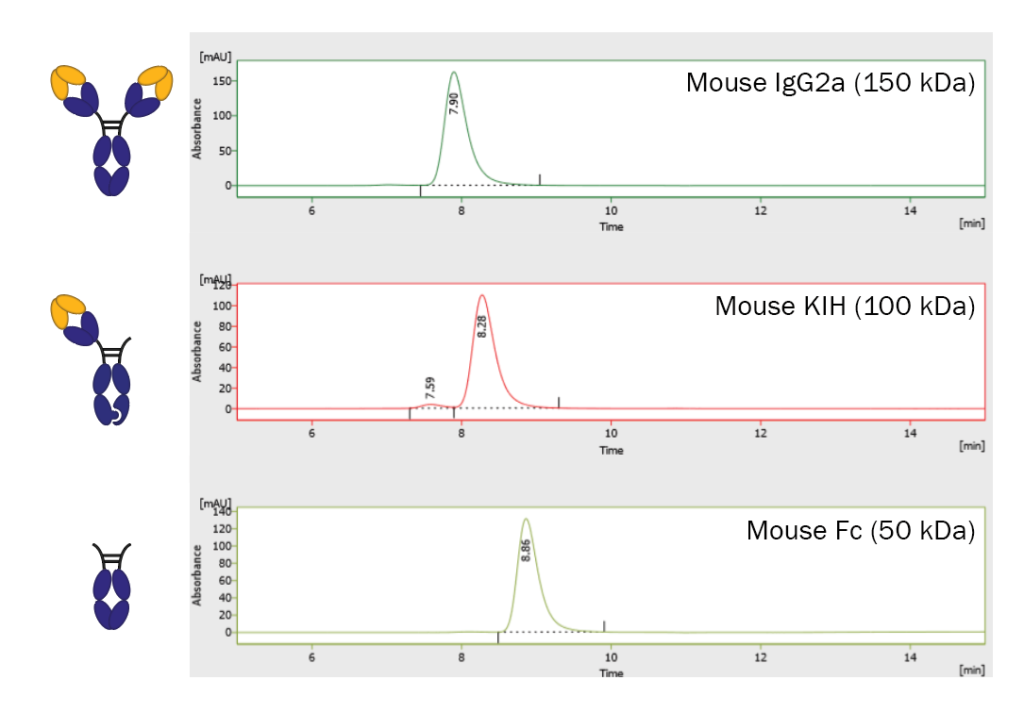
The knob-into-hole (KIH) format was a pioneering format permitting heavy-chain heterodimerization, creating an ‘IgG with two different arms’, and derivatives of it continue to play an important role in drug development. However, researchers have lacked syngeneic mouse models for evaluating bispecific combinations as the mutations applied to human IgG1 cannot be readily transferred to murine IgG subtypes.
To address this, Absolute Antibody has developed the first commercially available platform for the generation of fully murine bispecific antibodies. These antibodies have Fc domains with abrogated Fc gamma receptor binding, but they are fully capable of FcRn-mediated recycling. To overcome the light-chain pairing problem, single-domain binders were used on one IgG ‘arm’, where required through conversion of Fabs into scFvs.
We generated an anti-mCD3ε / TRp-1 bispecific, capable of selectively recruiting T-cells to TRP-1+ cancer cells for increased cytotoxic effector function as a proof of concept.

Conversion and production of an scFv from anti-mCD3ε clone 2C11, showing comparable activity to the parental hamster IgG.
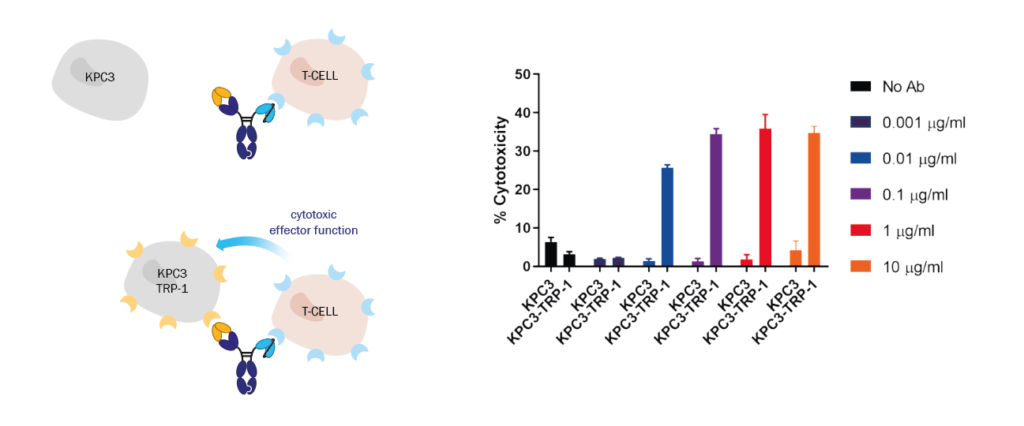
Combination of this anti-mCD3ε scFv into a bispecific T-cell engager, targeting TRP-1 on the Fab arm, lead to effective killing of transgenic TRP-1+ tumour cells, without any effect on the parental cell line.
Not your ideal pair of targets? Check out our range of available murine bispecifics in the table below. Get in touch with any questions or suggestions – we love to hear from you!
| Specificities | mCD3ε | mPD-L1 | mCD47 |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRP-1 | KIH | KIH | |
| HER2 | KIH | ||
| EGFR | KIH | ||
| EGFRvIII | KIH | ||
| mCD20 | KIH | ||
| mCTLA4 | KIH/IgG:dAb | IgG:dAb | |
| mPD1 | IgG:dAb | IgG:dAb | |
| mTIGIT | IgG:dAb | ||
| mVISTA | IgG:dAb | ||
| mCD200 | IgG:dAb |
Latest News
Upcoming Events
Please join us at the following conferences and events. Stop by our booth, or get in touch to arrange a meeting.
See All Dates
 United Kingdom (UK)
United Kingdom (UK)