The diversity of cells in the brain and nervous system of mammals is staggering. A brain map published in 2023 by an NIH-led data consortium finds more than 3,000 distinct neuron types in the human brain. Even though each cell carries the same set of genetic material, a cell can differentiate into a variety of neuronal types, changing how the brain processes and transmits information. To understand the inherent diversity of the brain and nervous systems, we recombinantly engineered antibodies that target key proteins in neuronal populations to identify and characterize neurons, like MAP-2 found in dendrites and synaptophysin found in presynaptic terminals. With various species, complete biological definition, and batch-to-batch reliability, recombinant antibodies against neuronal markers can help researchers identify neural subpopulations, map neural circuits, investigate neurodevelopment and plasticity, understand neurological disorders, and more. The following are recent citations using engineered antibodies from Absolute Antibody for neuronal marker research.
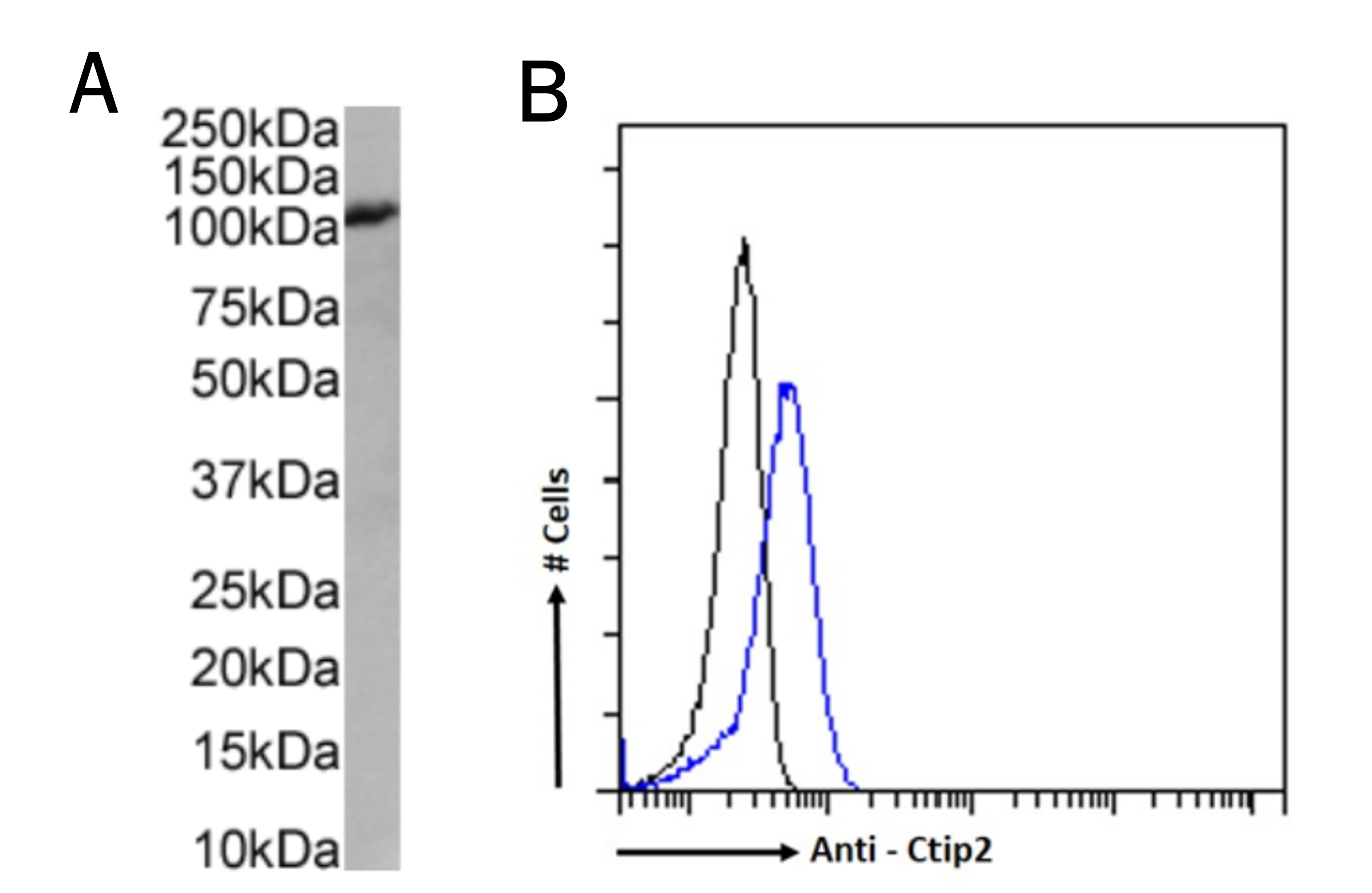
Western blot (A) and flow cytometry (B) using the Anti-Ctip2 antibody 25B6 (Ab00616).
Development of subdomains in the medial pallium of Xenopus laevis and Trachemys scripta: Insights into the anamniote-amniote transition
In this 2022 Frontiers of Neuroanatomy publication, researchers from the University of Madrid studied the brain development of the anamniote Xenopus frogs and the amniote Trachemys turtles by comparing neuronal populations using antibodies like Absolute Antibody’s anti-Ctip2 [25B6] recombinant antibody for immunofluorescence. They found that despite some differences in structure, both animals have similar brain regions responsible for memory and behavior. This suggests that there’s a basic blueprint for this part of the brain across different types of animals, showing how brains have evolved.
δ-Catenin controls astrocyte morphogenesis via layer-specific astrocyte–neuron cadherin interactions
This 2023 study focused on understanding how δ-catenin, a protein previously thought to be exclusive to neurons, influences the development of astrocytes, a type of brain cell. Researchers discovered that δ-catenin is highly expressed in astrocytes and interacts with N-cadherin, a cell adhesion protein crucial for astrocyte structure. Mutations in δ-catenin linked to autism reduced N-cadherin expression and affected astrocyte complexity. Silencing N-cadherin in astrocytes only affected the morphology of astrocytes in certain brain layers, suggesting δ-catenin’s role in regulating astrocyte development via N-cadherin interactions. Researchers used our recombinant engineered antibody clone 25B6 against Ctip2, a marker known to be found in lower brain regions, to differentiate between lower and upper-layer astrocytes in immunofluorescence assays in vitro.
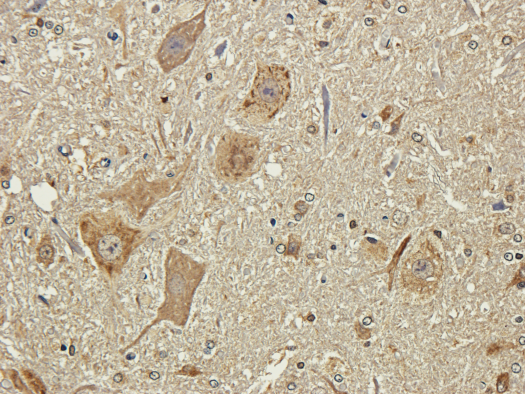
Immunohistochemical staining of rat spinal cord using anti-polysialic acid antibody Ab00240-23.0.
Neural cell adhesion molecule is required for ventricular conduction system development
This 2021 Development article explored the developmental biology of cardiac conduction by looking at the molecular pathways that lead to the formation and spacing of specialized cells in the ventral conduction system of the heart. Using Absolute Antibody’s recombinant anti-polysialic acid antibodies for immunofluorescence and western blot applications, researchers found that inhibiting polysialic acid’s post-translational modification of neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (NCAM-1) leads to improper formation and spacing of those cells. This study sheds light on the mechanisms of cardiac conduction development and disease, as well as more insight into the function of NCAM-1, a crucial protein in neural development.
Recombinant Engineered Antibodies
The Absolute Antibody catalog offers recombinantly produced antibodies against relevant proteins in neuronal marker research to ensure batch-to-batch reproducibility and enable antibody engineering. The antibodies are available off-the-shelf in different engineered formats, including mouse, rabbit, and human species, as well as various isotypes and fragments. The antibodies can also be custom-engineered into other formats upon request.
Our full catalog of neuroscience research antibodies is available on our Neuroscience Research Antibodies page. Additionally, if you can’t find what you need in our catalog, our antibody engineers can tailor any antibody or sequence to exactly what you need. Our custom services offerings include antibody engineering in every format, optimized antibody expression via our recombinant system, and antibody sequencing to protect your work.
We offer neuronal marker research reagents from other brands within our parent company Absolute Biotech:
- Goat polyclonal antibodies for neuronal markers like choline acetyltransferase, GFAP, and NMDA receptor from Everest Biotech
- MarathonRT ultra-processive reverse transcriptase for neuronal gene expression analysis from Kerafast.
- Neuronal nuclei (NeuN) antibodies, MAP-2 antibodies validated for IHC, and Calbindin antibodies and ELISA kits from LSBio.
Latest News
Upcoming Events
Please join us at the following conferences and events. Stop by our booth, or get in touch to arrange a meeting.
See All Dates
 United Kingdom (UK)
United Kingdom (UK)